NAFLD-related HCC has increasingly gained attention in medical research due to its complex nature and health implications. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent condition, potentially leading to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in severe cases. This article delves into the progression, risk factors, and recent advances in understanding and managing HCC associated with NAFLD.
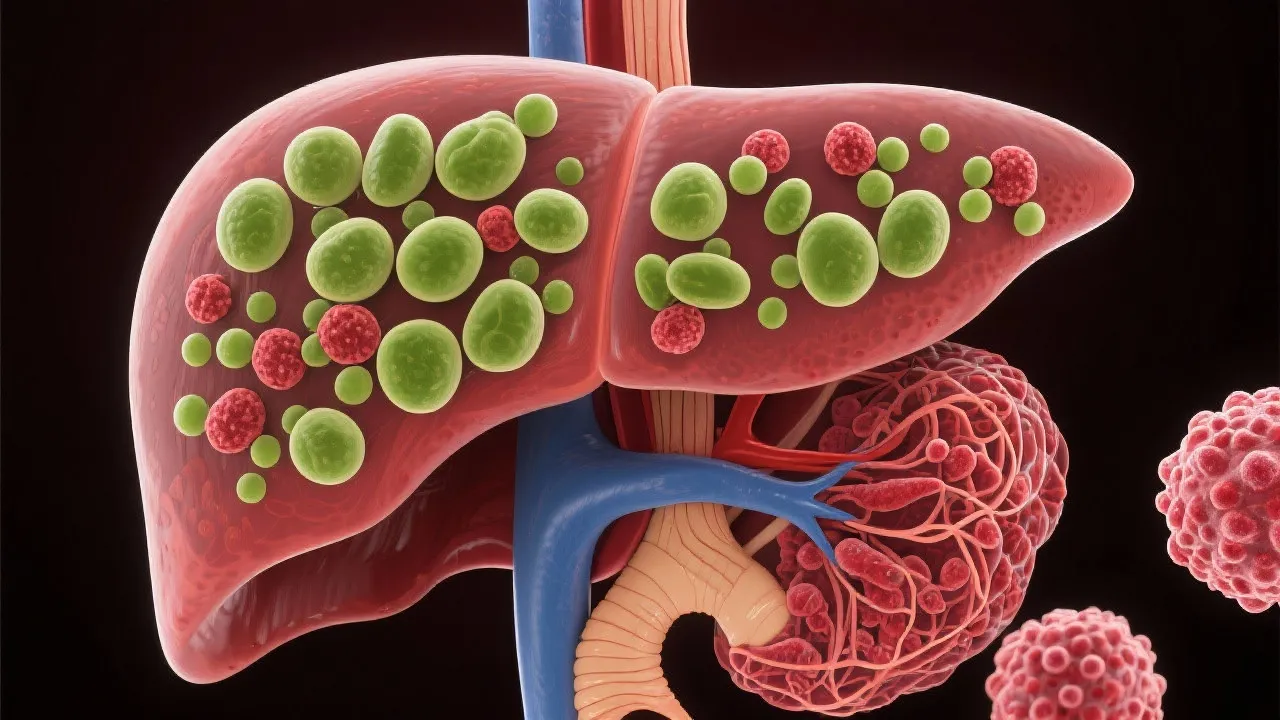
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is becoming increasingly recognized as one of the most prevalent liver disorders in Western countries, characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells in people who consume little or no alcohol. NAFLD can range from simple steatosis, where there is fat accumulation without inflammation or liver damage, to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which includes inflammation and liver cell injury. Over time, this condition can progress to more severe liver damage such as fibrosis (the buildup of scar tissue in the liver), cirrhosis (where the liver is severely scarred and cannot function properly), and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a form of liver cancer. HCC represents the lethal consequence of chronic liver disease and is associated with a significant risk of mortality.
The underlying mechanisms of NAFLD and its progression to HCC are complex and multifactorial. The initial step in NAFLD is the accumulation of fat in liver cells, often due to excessive caloric intake, sedentary lifestyle, and metabolic dysfunction. This fat accumulation triggers a cascade of inflammatory and fibrotic processes:
Understanding these processes is crucial in identifying therapeutic targets to prevent NAFLD's progression to HCC.
Numerous factors contribute to the risk of developing HCC in patients with NAFLD, along with direct consequences on both the lifestyle of individuals and medical management. One of the principal concerns is effectively identifying which individuals with NAFLD are at heightened risk of developing HCC. Research has identified several key risk factors, including:
Regular monitoring and management of these risk factors are crucial in mitigating the potential risk of progression to liver cancer. Notably, educational initiatives to promote healthy living can complement medical interventions and enhance individuals' awareness of their liver health.
Advances in imaging technologies and biomarkers have significantly enhanced the early detection of NAFLD-related HCC. Traditional approaches often relied heavily on liver biopsies and less sensitive imaging techniques. However, contemporary diagnostics now encompass several non-invasive methods that offer both accuracy and convenience:
As the field progresses, there is ongoing research into identifying biomarkers that can predict the onset of HCC more accurately, representing an essential direction for improving clinical outcomes. Increases in public and private funding for research in liver health are pivotal for developing these tools.
| Diagnostic Tool | Purpose | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| MRI-PDFF | Measures liver fat quantitatively | Non-invasive and accurate |
| FibroScan | Assesses liver stiffness | Quick assessment of fibrosis |
| Serum Biomarkers | Monitors disease progression | Potential for early intervention strategy |
Lifestyle changes, particularly in diet and physical activity, play a pivotal role in managing NAFLD. Not only do these modifications help prevent the condition from worsening, but they are crucial in mitigating the risk of HCC. Advocating for a proactive lifestyle includes:
Healthcare professionals play a fundamental role in guiding patients toward these lifestyle interventions, providing education, support, and resources to empower individuals to take charge of their health. The gradual adaptation of these changes ensures sustainability and improves adherence over time.
While lifestyle modifications are foundational in managing NAFLD, certain cases may necessitate pharmacological intervention. Medical treatment options are rapidly evolving, focusing on both controlling NAFLD and preventing its complications, including HCC. Recent pharmaceutical developments include:
Furthermore, combined approaches utilizing pharmacological agents along with lifestyle changes may yield better outcomes in liver health and reducing the risk of HCC. Continued research into the pharmacogenomics of NAFLD is critical for developing personalized approaches to treatment.
NAFLD-related HCC poses a substantial global health challenge. The burden of this disease is compounded by its silent progression and the increasing prevalence of obesity and metabolic disorders worldwide. As healthcare systems grapple with this epidemic, it is paramount to pursue coordinated international efforts in research, public health policy, and clinical management.
The future of NAFLD and HCC management will likely focus on several key areas:
As we continue to unravel the complexities of NAFLD and its links to hepatocellular carcinoma, a more profound understanding of its pathophysiology, combined with innovative research and integrated care models, will ultimately lead to improved outcomes for affected individuals across the globe.
In summary, the relationship between NAFLD and HCC represents a critical area for continued research, clinical innovation, and public health initiatives aimed at reducing the impact of liver disease on populations worldwide. By emphasizing early detection, personalized intervention, and aggressive management of risk factors, we can make significant strides in tackling this pressing health challenge.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
