This article explores the relationship between metabolic syndrome and its influence on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels, significantly increases the risk of developing NASH, a severe liver disease that can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, or hepatocellular carcinoma.
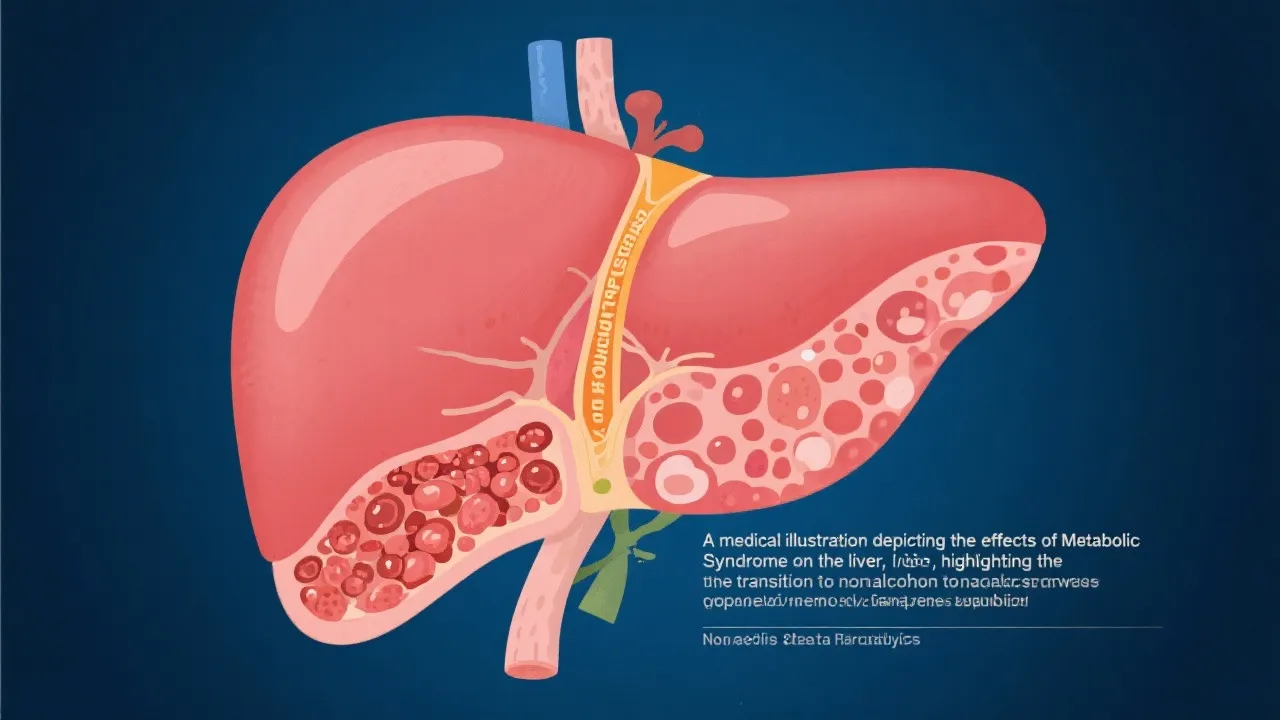
Metabolic syndrome is a complex condition characterized by a cluster of interrelated risk factors, significantly impacting global health. This syndrome is especially concerning, as it has a proven influence on developing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). NASH is a severe form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), marked by liver inflammation and damage that results from fat accumulation in liver cells. As lifestyles change and obesity rates continue to rise, understanding this intricate relationship becomes crucial for public health and individual well-being.
The primary components of metabolic syndrome include insulin resistance, abdominal obesity, dyslipidemia (abnormal lipid levels), hypertension (high blood pressure), and pro-inflammatory states. These elements do not act in isolation but collectively heighten the peril, especially concerning cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. Each factor is interrelated; for instance, insulin resistance often results from obesity, which in turn contributes to dyslipidemia and hypertension. Notably, these conditions also elevate the risk of developing NASH, transforming a fatty liver condition into a harmful state of chronic hepatic disease. The alarmingly high prevalence of metabolic syndrome, particularly in modern society, necessitates a deeper understanding of its components and their implications.
Insulin resistance serves as a cornerstone in the development of metabolic syndrome. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that facilitates glucose uptake by the body's cells. When cells become resistant to insulin, the pancreas compensates by producing more insulin, leading to higher insulin levels in the bloodstream, a condition known as hyperinsulinemia. This scenario has cascading effects on lipid metabolism, as elevated insulin levels promote fat accumulation in liver cells. The liver plays a central role in regulating various metabolic processes, and insulin resistance disrupts its function, driving the progression towards NASH. Thus, addressing insulin resistance is key in both managing metabolic syndrome and preventing NASH.
Abdominal obesity, often measured by waist circumference, is another critical component of metabolic syndrome. It indicates visceral fat accumulation, which is considered more metabolically harmful than subcutaneous fat. The fat stored in the abdominal cavity produces inflammatory cytokines and hormones that contribute to various metabolic complications. Individuals with abdominal obesity face increased stress on liver detoxifying responsibilities and are prone to hepatic steatosis, or the buildup of fat in liver cells. This condition is not benign; instead, it paves the way for further inflammation and scarring, culminating in NASH. Therefore, addressing abdominal obesity is essential in managing not only metabolic syndrome but also preventing the progression to more severe liver diseases.
Dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated levels of triglycerides and low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, is another vital aspect of metabolic syndrome. Altered lipid profiles can lead to the accumulation of fatty acids in the liver, worsening steatosis and promoting inflammation. Enhanced triglyceride synthesis in the liver, facilitated by insulin resistance, contributes to fat deposition in liver cells. Furthermore, low HDL cholesterol levels complicate matters; HDL is often referred to as 'good cholesterol' due to its role in transporting excess cholesterol from the liver to be metabolized or excreted. When HDL levels are low, the liver cannot effectively clear accumulated lipids, exacerbating NASH progression. Strategies to improve lipid profiles through dietary changes, physical activity, or pharmacological interventions are critical in advancing health outcomes.
Hypertension is a well-known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, but its role in metabolic syndrome also fuels the risk of developing liver diseases like NASH. High blood pressure is often associated with endothelial dysfunction, which hampers blood flow and nutrient delivery to the liver, aggravating its already compromised state due to fat overload and inflammation. Moreover, hypertension is commonly linked with pro-inflammatory states, creating an environment conducive to liver cell injury. The connection between hypertension, inflammation, and liver health signifies the need for comprehensive lifestyle modifications aimed at managing blood pressure and improving overall metabolic health.
Clinical studies have affirmed a strong correlation between the components of metabolic syndrome and the onset of NASH. Individuals with metabolic syndrome are significantly more likely to develop NASH than those without it. For instance, clinical trials indicate that more than 85% of individuals with diagnosed NASH manifest at least one component of metabolic syndrome, illustrating the high interrelation rate. As metabolic syndrome progresses, the risk of hepatic inflammation and scarring increases, demonstrating a clear pathway from metabolic dysregulation to liver disease enhancement. Understanding this link is paramount for both clinicians and patients, enabling early intervention and strategic management tailored to mitigate risks associated with NASH.
To grasp the connection between these two conditions, it is crucial to understand how the components of metabolic syndrome alter liver function and health. Excessive free fatty acids in the liver due to lipid overflow compromise liver function, instigating steatosis. When combined with insulin resistance, these stress substrates further the inflammatory response, inducing hepatocyte injury and fibrogenesis—hallmarks of NASH. This intricate interplay describes a vicious cycle: as liver fat accumulates, it incites an inflammatory response that promotes further fat infiltration and liver damage.
An important aspect of this pathophysiological process is the concept of "two-hit hypothesis." The first hit refers to the accumulation of fat in the liver, which, while initially reversible, creates a susceptible environment for injury. The second hit involves the inflammatory and fibrotic response to this fat accumulation, leading to oxidative stress and hepatocyte apoptosis (programmed cell death). This duality suggests that both lifestyle modifications aimed at reducing fat and targeted interventions toward alleviating inflammation are integral in halting and potentially reversing the progression from simple steatosis to NASH.
A multitude of research endeavors have probed the direct and indirect causes linking metabolic syndrome to NASH. For example, a study published in the "Journal of Hepatology" found that over 85% of individuals with NASH manifest at least one component of metabolic syndrome. Other investigations focus on the roles of diet, exercise, and pharmaceuticals in altering the disease trajectory. There's ongoing research into the impact of specific dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, on metabolic health and liver function. Studies suggest that adopting such diets can significantly reduce markers of liver inflammation and improve metabolic parameters.
Moreover, advancements in pharmacotherapy are being explored to specifically target liver health. Drugs such as pioglitazone and vitamin E have shown promise in treating patients with NASH, especially those without diabetes. These medications aim to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce liver inflammation, respectively, highlighting the need for continued exploration of pharmacological options. As these research trajectories evolve, a clearer understanding of the mechanisms linking metabolic syndrome and NASH will emerge, paving the way for smarter therapeutic strategies.
Diagnosis of NASH related to metabolic syndrome necessitates a comprehensive approach, often involving liver biopsies, advanced imaging techniques like elastography, and rigorous blood tests to monitor liver enzymes and assess systemic inflammation. The presentation of NASH can often be insidious, necessitating a high index of suspicion, especially in individuals with known metabolic syndrome. Often, specialists deploy a combination of these methods to discern the disease's presence and progression accurately. Early diagnosis is vital as it can lead to timely intervention and potentially halt further liver damage.
| Diagnostic Test | Description | Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Liver Biopsy | Extraction of liver tissue for microscopic analysis. It remains the gold standard for confirming NASH diagnosis and assessing the extent of liver inflammation and fibrosis. | High |
| Elastography | Non-invasive imaging to assess liver stiffness, which correlates with fibrosis stage. It offers an accurate snapshot of liver health without the need for invasive procedures. | Moderate to High |
| Blood Tests | Measure liver enzymes like ALT, AST, and other markers of liver function and inflammation. It serves as an initial screening tool but lacks specificity for NASH diagnosis. | Moderate |
The combination of these diagnostic modalities provides a robust framework for assessing liver health. However, ongoing research into non-invasive biomarkers is also valued to identify individuals at risk of NASH without necessitating invasive procedures. These biomarkers could complement existing strategies, providing a more comprehensive understanding of liver pathology and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding the nexus between metabolic syndrome and NASH has driven advancements in preventive health strategies. Lifestyle modifications, particularly those targeting weight reduction, improved physical activity, and dietary changes, have been pivotal. Interventions aimed at achieving even small amounts of weight loss, around 5-10%, can significantly improve liver health and reduce steatosis. Exercise is particularly beneficial, not only for weight management but also for enhancing insulin sensitivity and improving lipid profiles.
Medications regulating blood lipid levels and insulin sensitivity also form a cornerstone of therapeutic interventions. For instance, statins are often prescribed to manage dyslipidemia, while metformin may be utilized to enhance insulin sensitivity in patients with concurrent diabetes. Additionally, the emerging portfolio of drugs specifically targeting NASH and liver inflammation implies that tailored therapeutic strategies will soon be available for patient management.
Behavioral interventions that incorporate nutritional counseling can enhance compliance and effectiveness of lifestyle changes. Programs such as weight watchers or community-based fitness initiatives can serve as valuable adjuncts to clinical interventions. These approaches not only focus on dietary changes but also provide social support, which is critical for sustained lifestyle modifications. Early education about the risks of metabolic syndrome and NASH encourages individual accountability and proactive health management.
Q: What exactly causes NASH?
A: NASH is predominantly caused by an accumulation of fat in liver cells leading to inflammation and cell damage. Often, it is closely linked to metabolic syndrome, wherein various metabolic dysregulations contribute to liver inflammation.
Q: How is NASH different from simple fatty liver disease?
A: While simple fatty liver involves fat accumulation in the liver without inflammation, NASH involves both fat build-up and liver inflammation, potentially leading to significant liver damage and complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Q: Can metabolic syndrome be reversed?
A: Yes, metabolic syndrome can often be effectively managed and even reversed through lifestyle changes such as diet improvements, physical activity, and sometimes medications that improve insulin sensitivity and lipid profiles.
Q: What role does diet play in managing metabolic syndrome and NASH?
A: Diet plays an essential role in managing metabolic syndrome and NASH. A balanced diet emphasizing whole foods, fibers, healthy fats, and limiting refined sugars can help regulate body weight, improve metabolic health, and support liver function.
Q: How often should individuals at risk for NASH be monitored?
A: Individuals at risk for NASH, particularly those with metabolic syndrome, should have regular check-ups. This includes monitoring liver enzymes through blood tests annually and, if needed, non-invasive imaging every couple of years to assess liver health and progression.
The mutual interactions between metabolic syndrome and NASH highlight a crucial health concern that demands awareness and proactive management strategies. While ongoing research continues to unpack the intricacies of this association, the role of preventive healthcare pertaining to metabolic health has never been more paramount. Addressing lifestyle factors associated with metabolic syndrome can significantly mitigate the risk of developing NASH, thus enhancing overall well-being and improving public health outcomes. It is clear that a combination of early detection, lifestyle interventions, and pharmacological strategies promises a more hopeful trajectory in managing both metabolic syndrome and the associated liver conditions.
As the understanding of metabolic syndrome and its impact on liver health continues to evolve, future research is needed to explore novel therapeutic strategies and preventive measures. Research initiatives may focus on elucidating the molecular mechanisms that underpin the connection between metabolic disturbances and liver inflammation, which could lead to the identification of new drug targets. Furthermore, there is a critical need for large-scale studies that investigate the long-term effects of lifestyle interventions, pharmaceutical treatments, and dietary modifications on both metabolic syndrome and NASH.
Public health policies geared toward obesity prevention, health education, and access to healthy foods are key to combating the epidemic of metabolic syndrome and its liver-related consequences. Governments and health organizations must prioritize programs that promote healthy lifestyle choices, particularly in populations at greater risk of metabolic syndrome. Initiatives that facilitate community engagement and improve access to resources for nutritious foods, physical activity, and healthcare can profoundly influence outcomes at a population level.
Ultimately, a multidisciplinary approach, integrating clinical expertise, research, and public policy, is essential to mitigate the growing burden of metabolic syndrome and NASH. By fostering collaboration across healthcare providers, researchers, and policymakers, effective strategies can be developed to enhance liver health and overall metabolic well-being for future generations.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
