Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis, or NASH, is an intricate progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease that involves liver inflammation and damage. As a significant health concern, NASH often develops due to a buildup of fat in the liver, independent of alcohol consumption. This article delves into its complexities, offering insights into its causes, implications, and prevailing treatment approaches within the medical community.
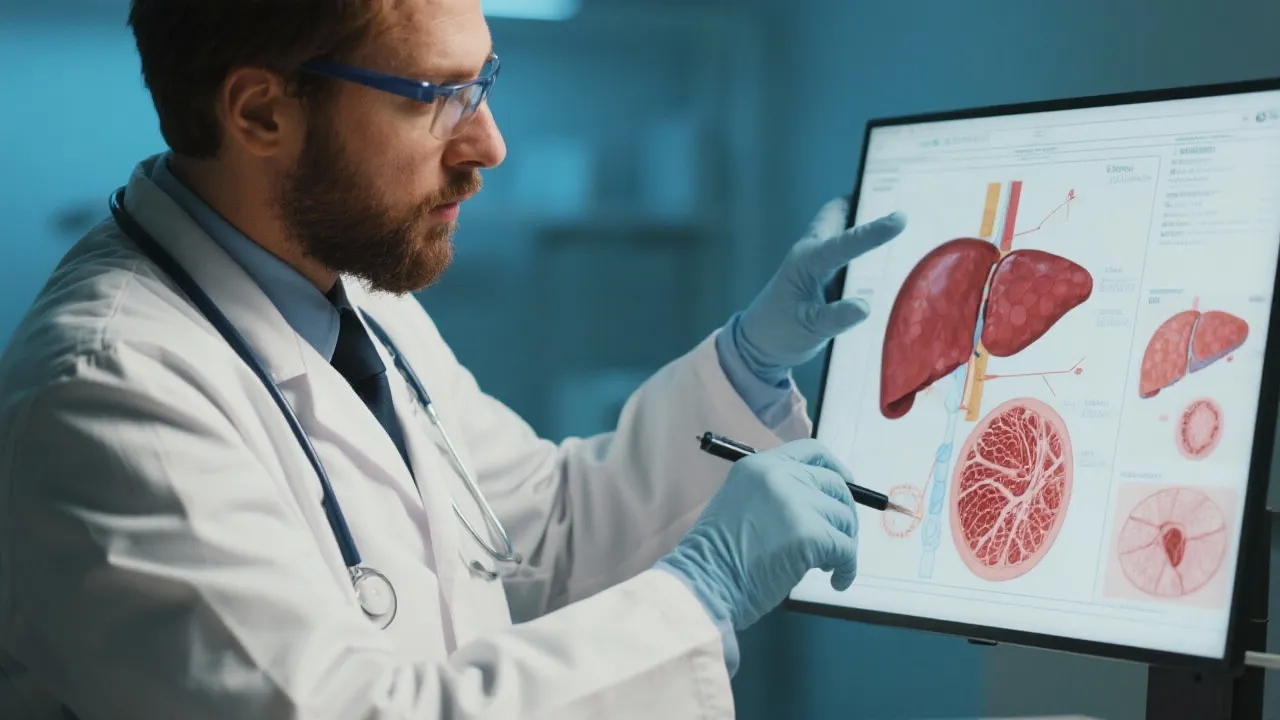
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) is a liver condition that is garnering attention among medical professionals worldwide. It represents a spectrum of liver diseases characterized by inflammation and fibrosis, emerging as a silent threat due to its escalation into severe liver disorders. Frequently an unseen enemy, NASH requires early diagnosis and intervention to prevent negative health consequences.
As obesity and metabolic syndrome prevalence continue to rise globally, NASH has become more common, posing a significant public health challenge. Recent studies have shown that NASH can lead to hepatic fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma, making awareness and understanding of this condition crucial. Additionally, NASH is not limited to certain demographic groups and can present in individuals of all ages, including children, making it a widespread concern.
NASH is primarily caused by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, leading to inflammation and cell damage. While its exact causes remain a subject of extensive research, several risk factors have been identified. These include obesity, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and high cholesterol levels. The interplay of these risk factors with lifestyle choices plays a significant role in the development and progression of NASH.
Additional factors contributing to the risk include genetic predisposition, with certain ethnic groups, such as Hispanics and African Americans, showing higher susceptibility to NASH. Furthermore, age is a notable risk factor as the prevalence of NASH increases with advancing age. Emerging evidence suggests that sleep apnea may also contribute to the exacerbation of NASH symptoms, indicating the multifactorial nature of this disease.
As modern lifestyles shift toward sedentary practices and high-caloric diets, the prominence of these risk factors is increasing, elevating the prevalence of NASH in the population. Public awareness campaigns aimed at addressing the lifestyle choices that contribute to these risk factors are essential in preventing the further rise of NASH cases.
One of the challenges presented by NASH is its asymptomatic nature in the early stages. Many individuals remain unaware of the disease until it progresses to more serious conditions, such as cirrhosis or liver cancer. Symptoms, when they appear, may include fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice, and unexplained weight loss. Other symptoms, including itching, swelling in the legs, and an enlarged liver, can also become apparent as the disease progresses.
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of blood tests, imaging studies, and liver biopsy, the latter being the gold standard for confirming NASH. Blood tests may reveal elevated liver enzyme levels, while imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI can assess fat accumulation in the liver. However, while these methods can detect fat in the liver, only a liver biopsy can definitively determine the presence of inflammation and fibrosis. This is crucial since only about 10 to 30% of individuals with fatty liver will progress to NASH.
Due to the often vague presentation of symptoms, healthcare providers are encouraged to consider NASH in individuals with relevant risk factors, even in the absence of pronounced symptoms. Utilizing non-invasive scoring systems can also aid in identifying patients who may be at higher risk for liver damage due to NASH.
Management of NASH revolves around addressing underlying lifestyle factors. Weight reduction through a combination of diet and exercise has been shown to improve liver histology in patients. Studies indicate that losing as little as 5-10% of body weight can lead to significant improvements in liver health. Implementing a balanced diet rich in nutrients and low in saturated fats and sugars is vital for achieving these weight loss goals. Dietary patterns such as the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins, are often recommended for those with NASH.
In addition to lifestyle changes, managing diabetes, hypertension, and cholesterol levels is crucial in controlling the disease's progression. Medications for diabetes and hyperlipidemia should be adjusted and optimized to minimize the strain on the liver. Continuous monitoring of liver function tests is recommended for patients with diagnosed NASH to assess the effectiveness of management strategies.
Pharmacological treatments are being researched extensively, with numerous clinical trials underway. Some medications, such as vitamin E and pioglitazone, have shown promise in clinical settings; however, no specific medication is yet approved for treating NASH. The ongoing research holds promise for future therapeutic options that will tackle the underlying pathophysiology of the disease, potentially transforming the management landscape of NASH.
Additionally, creating a supportive environment for patients to succeed in making lifestyle changes is paramount. Health care teams may include nutritionists, dietitians, and exercise physiologists who can provide tailored plans and resources. Psychological support is also essential, as managing a chronic condition can be overwhelming and affect mental health. Addressing barriers to lifestyle changes through counseling, support groups, and educational resources can significantly enhance overall outcomes.
Healthcare providers play a critical role in combating NASH by promoting awareness and early intervention. They are tasked with identifying at-risk individuals and providing guidance on lifestyle modifications. Primary care physicians, endocrinologists, and hepatologists all have pivotal roles in raising awareness and improving patient outcomes. Continuous education and staying updated with the latest research are imperative for medical professionals aiming to mitigate the impact of this expanding clinical entity.
Health care providers must be equipped to conduct thorough evaluations and implement screenings for high-risk populations. For instance, routine assessments for liver disease in patients with obesity or metabolic syndrome can help enable early diagnosis. Integrating discussions about liver health into routine health visits can further familiarize patients with NASH and its implications.
Furthermore, healthcare systems can enhance their protocols by incorporating standard screening procedures and ensuring that staff members are trained to recognize the signs of NASH. Additionally, collaborations with dietitians and physical trainers can result in comprehensive care strategies that prioritize lifestyle changes. Telemedicine can also enhance accessibility to specialized care for patients, particularly in underserved areas.
Ultimately, the journey toward effective management and treatment of NASH involves a multipronged approach. By fostering a culture of awareness in patients and among healthcare workers, the medical community can make strides against the epidemic of NASH.
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis stands as an expanding clinical entity with serious implications for global health. Understanding its causes, recognizing early symptoms, and committing to preventive measures are key strategies in tackling this liver disease. As the medical community continues to explore solutions, patient education and proactive health management remain pivotal in alleviating the burden of NASH.
Looking forward, global collaborations are necessary for advancing research, creating effective prevention programs, and establishing comprehensive treatment guidelines. With the rising incidence of NASH , an integrated approach between healthcare systems, educational institutions, and community organizations can foster both awareness and solutions.
As society progresses through the challenges presented by an increasing prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases, the understanding and management of NASH will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping the future of liver health. The fight against NASH is not just a clinical endeavor but a public health imperative that requires collective action from all stakeholders involved.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
