Hepatitis E is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis E virus, often resulting in inflamed liver conditions. In severe cases, it may necessitate a liver transplant. Here, we explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, with a focus on liver transplantation as a critical intervention for acute liver failure induced by this virus. The complexities of managing hepatitis E in clinical settings are also discussed.
Hepatitis E is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver, leading to a variety of symptoms including jaundice, fatigue, nausea, and abdominal pain. This condition arises due to the hepatitis E virus (HEV), which is often transmitted through the consumption of contaminated water. This makes it a formidable health concern, particularly in regions with inadequate sanitation and insufficient access to clean drinking water. Hepatitis E is unique among the hepatitis viruses due to its high incidence in certain populations and its association with sporadic and epidemic outbreaks. While most cases of Hepatitis E are self-limiting and resolve on their own without the need for specific antiviral treatment, there are instances where the infection can progress to fulminant hepatitis, which can lead to acute liver failure. Acute liver failure is a life-threatening condition characterized by the rapid deterioration of liver function, necessitating immediate medical intervention.
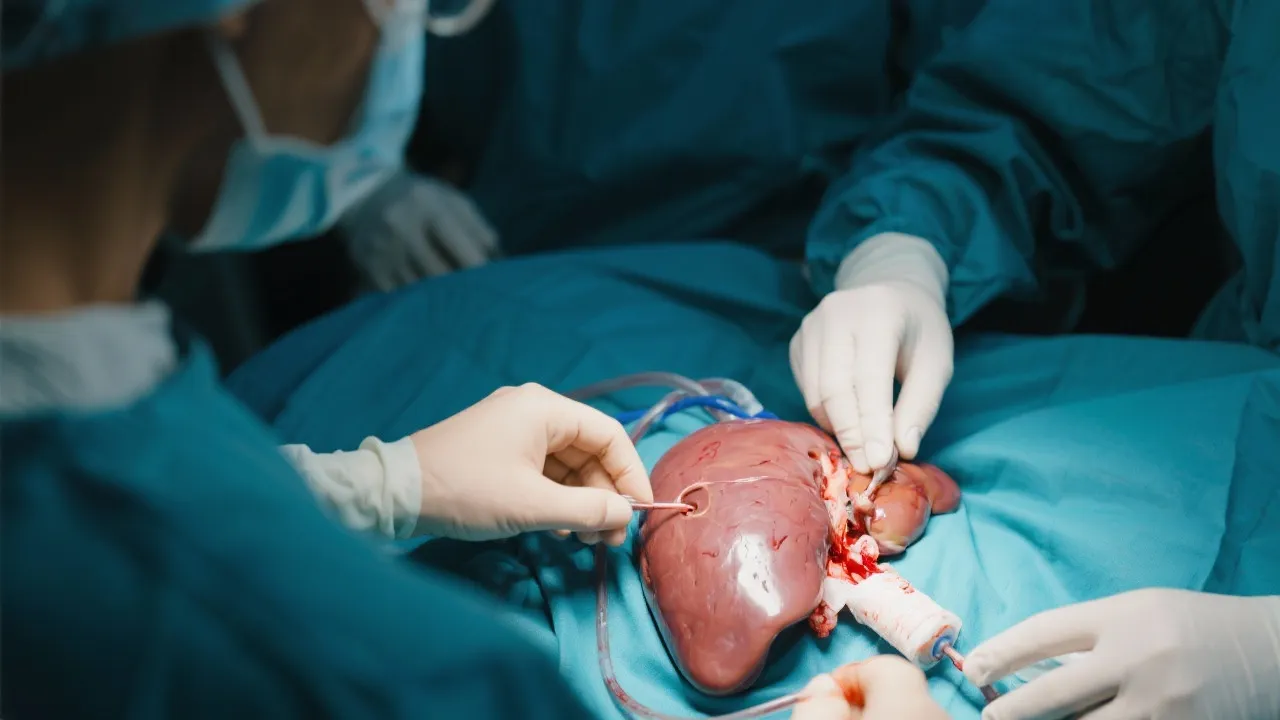
When hepatitis E leads to acute liver failure, a liver transplant may become a necessary and life-saving intervention. During a liver transplant, the diseased liver is replaced with a healthy organ from a deceased donor or from a living donor whose liver can regenerate. This procedure can dramatically improve the patient's quality of life and survival prospects, but it is not without its complexities. The process of evaluating a patient for a liver transplant involves thorough assessment and decision-making by a multidisciplinary team, which includes hepatologists, transplant surgeons, and other healthcare professionals. Significant considerations include the severity of liver disease, the presence of any other comorbid conditions, and the likelihood of the patient adhering to post-transplant care and lifestyle modifications.
| Stage | Details |
|---|---|
| Initial Infection | The virus enters the body, often unnoticed at first, when consuming contaminated water or food. There may be an incubation period lasting from a few weeks to several months, during which the virus multiplies without causing symptoms. |
| Acute Stage | Symptoms begin to manifest, typically occurring between two to ten weeks after infection, including jaundice and elevated liver enzymes, indicating liver distress. Patients may also report flu-like symptoms such as body aches, fever, and malaise. |
| Severe Complications | In some cases, particularly in vulnerable populations like pregnant women or immunocompromised individuals, the disease can progress rapidly to liver failure. This stage is marked by acute decompensation, hepatic encephalopathy, and multi-organ failure, necessitating urgent medical intervention. |
Liver transplants are considered in critical conditions where the liver has lost its functional capacity due to severe damage from diseases such as hepatitis E. The decision to place a patient on the waiting list for a liver transplant is made after a comprehensive evaluation encompassing multiple aspects of health. Medical specialists assess various factors including the severity of liver damage as determined by the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score, overall health status, and psychological readiness for surgery. Additionally, the patient’s age, existing medical conditions, and previous responses to treatments are all critical components of the evaluation process. The liver transplant candidacy process is lengthy and intricate, ensuring that only those who are likely to benefit from a transplant proceed to surgery. The timing of a liver transplant is crucial; too late, and the risk of complications increases drastically, but too soon can lead to unnecessary surgery risks.
Preventive measures are vital in managing hepatitis E, especially in regions prone to outbreaks. To significantly reduce transmission rates, improving sanitation infrastructure is fundamental. This includes ensuring access to clean, safe drinking water, proper sewage disposal, and hygiene practices such as frequent hand washing. Public health campaigns that educate communities about hygiene and food safety can drastically lower the incidence of hepatitis E. Community-level approaches, such as constructing water purification systems and training local populations in safe food preparation methods, are effective strategies in outbreak prevention. In terms of treatment, supportive care remains the cornerstone of managing hepatitis E infections. Patients are advised to maintain hydration, consume a nutritious diet, and avoid alcohol to allow the liver to recover. In severe cases, when hepatitis E leads to acute liver failure, liver transplantation might be imminent and is considered a life-saving intervention.
Liver transplantation presents numerous challenges that healthcare systems face. One of the most pressing challenges is the scarcity of donor organs, which can delay lifesaving treatment for patients. The gap between the number of individuals needing transplants and the availability of suitable organs has resulted in long waiting lists in many countries. The risk of rejection is another significant hurdle; post-transplant, patients must adhere to immunosuppressive regimens to prevent their immune systems from attacking the transplanted liver. Managing these regimens is a delicate balance, as inadequate immunosuppression can lead to organ rejection, while excessive immunosuppression increases the risk of infections and other complications. Additionally, access to healthcare and the costs associated with liver transplantation can be substantial barriers, particularly in developing regions where hepatitis E is prevalent. The high expense of transplant surgeries and subsequent lifelong medication necessary for adherence to immunosuppression protocols may deter patients from pursuing this potentially life-saving option.
In conclusion, understanding hepatitis E and its potential to necessitate liver transplants is crucial for both healthcare practitioners and at-risk populations. By improving sanitary conditions and advancing public health education, the incidence of severe cases can be minimized, thereby reducing the need for complex medical interventions such as liver transplants. The integration of public health strategies aimed at reducing hepatitis E transmission combined with advancements in medical interventions provides a comprehensive approach to tackling this public health challenge. As research progresses, new methods of prevention and treatment continue to evolve, offering hope for better management of this significant public health concern. The engagement of communities, healthcare professionals, and policymakers in these efforts will be essential to make strides against hepatitis E and its associated health impacts.
Research efforts in hepatitis E are increasingly focused on understanding the virology, epidemiology, and potential treatment modalities for this viral infection. Scientists are exploring various facets of the virus, including its transmission dynamics, the immune response elicited by infection, and the development of effective vaccines. A significant research interest is the characterization of different HEV genotypes, with studies indicating that various strains may differ in virulence and epidemiological features. This has implications for vaccine development and efficacy, as well as for public health responses tailored to specific regions and populations.
Furthermore, the role of zoonotic transmission, particularly among swine and other animals, is an area that warrants further investigation. It has been suggested that certain strains of HEV disseminate from animal reservoirs to humans, and understanding how this occurs could inform preventive strategies. Collaboration between veterinarians, public health officials, and researchers is critical for designing comprehensive surveillance systems that can track zoonotic HEV transmission pathways.
In terms of treatment, there is a pressing need for antiviral therapies that specifically target HEV and can be used in conjunction with supportive care. Current treatment options are limited primarily to symptomatic management, and the development of effective antiviral agents would be a significant advancement in the field. Continued clinical trials and research initiatives aimed at elucidating the mechanism of action of potential antiviral compounds are essential for bringing new treatment options to the forefront.
Additionally, long-term studies monitoring patients post-hepatitis E infection are necessary to gain insights into the persistent effects of the virus, particularly in individuals who have experienced acute liver failure. Research into genetic predispositions that may affect the severity of illness in different populations could further elucidate factors contributing to outcomes in hepatitis E cases.
As we continue to explore the intricacies of hepatitis E, the importance of a multi-faceted approach involving prevention, treatment, and research cannot be overstated. Concerted efforts from health authorities, researchers, and communities are vital in curbing the incidence of hepatitis E and protecting vulnerable populations. By investing in public health initiatives, enhancing sanitation infrastructure, and promoting vaccination awareness where available, we can pave the way for a future with reduced morbidity and improved outcomes in hepatitis E cases. Only through sustained engagement and innovation can we hope to address the ongoing challenges posed by this viral infection and safeguard public health effectively.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
