Exploring the complex relationship between Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) unveils a pressing healthcare challenge. NAFLD is a prevalent liver condition that can evolve into HCC, a primary liver cancer. This guide scrutinizes current research, presenting insights into pathogenesis, risk factors, and prevention strategies, essential for medical professionals and researchers.
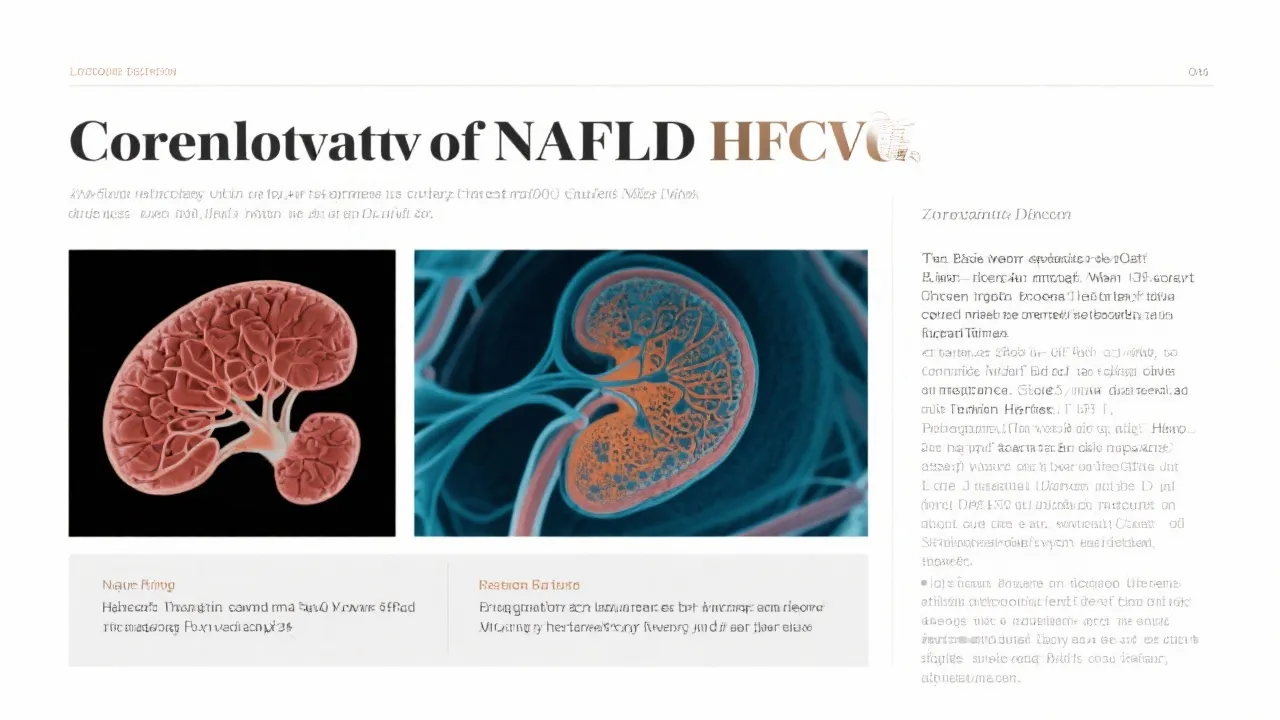
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) emerges as a leading cause of chronic liver disease globally, driven predominantly by lifestyle factors such as obesity and metabolic syndrome. Its significance intensifies given its potential progression to Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), the very common type of primary liver cancer. Understanding the link between NAFLD and HCC is crucial for early intervention and improving patient outcomes. As the global burden of obesity escalates, the understanding and management of NAFLD and its ramifications become ever more critical.
NAFLD affects an estimated 25% of the global population, posing a significant burden on healthcare systems. Characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells without significant alcohol consumption, NAFLD can progress to Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and ultimately HCC. The condition's prevalence is expected to rise, paralleling increasing obesity rates. In the United States alone, the prevalence of NAFLD is estimated to approach 30%, highlighting the urgent need for public health strategies focused on prevention and early detection.
The economic implications of NAFLD are considerable as well. The rising prevalence places a strain on healthcare resources, with increasing hospitalizations, liver transplantations, and associated costs. In addition to the direct healthcare costs, NAFLD leads to loss of productivity and reduced quality of life for affected individuals. These realities underline the need for preventative measures and effective management strategies to mitigate the rising tide of this disease.
The transition from NAFLD to HCC involves complex pathogenetic mechanisms. Chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and cellular injury from ongoing lipid accumulation play pivotal roles. Research indicates that insulin resistance, genetic predispositions, and altered gut microbiota further contribute to disease progression. Understanding these mechanisms is fundamental in developing therapeutic strategies.
Oxidative stress is particularly noteworthy as it results from an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and antioxidant defenses, leading to cellular damage. This is coupled with inflammatory processes mediated by cytokines, which can promote the transformation of benign liver lesions into malignant ones. The involvement of the gut-liver axis also represents a fascinating area of research, suggesting that the gut microbiome may influence liver health through alterations in metabolism and immune response.
Moreover, genetic polymorphisms have been associated with the severity of liver disease and the risk of progression to HCC. For example, variations in genes responsible for lipid metabolism, inflammatory responses, and fibrogenesis can increase individual susceptibility to NAFLD and its malignant transformation. Targeting these specific pathways might offer new avenues for intervention.
Identifying individuals at risk for developing HCC from NAFLD requires a comprehensive assessment of metabolic factors, liver histology, and genetic markers. Advanced diagnostic techniques, including imaging modalities such as ultrasound, elastography, and MRI, as well as biomarker analyses, are vital for early detection and regular monitoring. Increased vigilance is warranted for patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis.
The use of non-invasive tests has gained traction, allowing for the assessment of liver stiffness and steatosis without resorting to invasive biopsies. These methods not only enhance the patient experience but also expand the options for routine screening, particularly for high-risk populations such as individuals with type 2 diabetes or significant obesity.
Moreover, the advent of genetic testing introduces a promising dimension to risk stratification. Understanding an individual's genetic background may allow healthcare providers to identify those at heightened risk for progression from NAFLD to HCC, enabling personalized surveillance and management strategies.
Screening recommendations vary by clinical practice guidelines, but a common theme is the importance of routine follow-up for at-risk populations, particularly individuals with advanced fibrosis, who demonstrate significantly higher rates of HCC. The utilization of a multidisciplinary approach involving dietitians, hepatologists, and primary care providers is essential for optimizing patient outcomes.
Lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss, dietary changes, and regular physical activity, are pivotal in NAFLD management. Evidence suggests that even modest weight loss can significantly improve liver health and reduce the risk of disease progression. Nutritional interventions focusing on balanced diets low in carbohydrates and saturated fats show promise in managing NAFLD and improving liver enzymes.
Pharmacological therapies targeting metabolic pathways and inflammation are under investigation. Current pharmacologic agents include insulin sensitizers, lipid-lowering drugs, and new agents showing promising results in clinical trials. Medications like pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione, have been studied for their efficacy in improving liver histology in patients with NASH.
For advanced cases progressing to HCC, surgical resection, liver transplantation, or locoregional therapies might be considered, alongside traditional systemic therapies. Surgical options, however, are primarily reserved for patients with well-compensated liver disease and early-stage tumors. Liver transplantation remains the only curative option for individuals with decompensated cirrhosis and HCC, emphasizing the need for timely referral to transplant centers.
The synergy between lifestyle interventions and pharmacologic therapy may yet elucidate the best treatment pathways for patients. As more is learned about the disease's complex biology, personalized treatment modalities that account for factors like age, comorbid conditions, and genetic predispositions could emerge, leading to improved outcomes for patients affected by NAFLD and HCC.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| NAFLD | Excessive fat in liver cells without alcohol influence. |
| NASH | Advanced form of NAFLD with inflammation and damage. |
| Cirrhosis | Scarring of the liver, increasing HCC risk. |
| HCC | Liver cancer originating from hepatocytes. |
| Fatty Liver | Accumulation of fat in the liver without significant damage. |
| Fibrosis | Formation of scar tissue due to liver injury. |
Ongoing research is crucial in unraveling novel biomarkers for early detection and therapeutic targets. Studies into genetic variants and their influence on disease progression are promising. Moreover, advanced imaging techniques, such as 3D ultrasound and elastography, offer enhanced precision in monitoring NAFLD-related liver changes, vital for timely interventions in high-risk groups. Genetic testing, including single-nucleotide polymorphisms, has the potential to risk-stratify patients effectively and guide clinical decision-making.
Additionally, the exploration of metabolic and inflammatory pathways continues to provide insights into NAFLD's progression to HCC. Investigations into the role of the intestinal microbiome may reveal new therapeutic targets as well, highlighting the interconnectedness of our body's systems.
Clinical trials are increasingly focusing on long-term outcomes, seeking to validate early intervention strategies and optimize treatment approaches for both NAFLD and HCC. The integration of artificial intelligence in imaging analysis is an emerging field that shows promise in automating the assessment of liver health, allowing for earlier and more accurate diagnosis of at-risk patients.
As the science evolves, collaboration among clinicians, researchers, and public health officials will be imperative in developing comprehensive strategies that address the multifaceted nature of NAFLD and HCC. An emphasis on preventive measures, education, and health policies that promote awareness of liver disease is crucial in addressing this burgeoning public health crisis.
NAFLD and its malignant transformation into HCC epitomize a growing healthcare crisis. The condition's global prevalence necessitates collaborative efforts in research, patient education, and healthcare policy development. Preventive strategies emphasizing lifestyle changes could significantly reduce the incidence and progression of this disease. The rising burden of health care costs associated with chronic liver diseases calls for escalated awareness campaigns targeting at-risk populations alongside healthcare provider training programs, ensuring timely diagnosis and management.
Countries are increasingly recognizing NAFLD as a public health issue that intersects with rising obesity rates and diabetes prevalence. Thus, implementing community-wide health initiatives aimed at promoting healthy lifestyles through nutritional programs and regular physical activities is paramount. Schools, workplaces, and healthcare systems must work in tandem to cultivate environments that encourage healthy behavior and routine health screenings.
The enactment of policies supporting health education and access to healthcare services can make a meaningful difference in the lives of individuals at risk for NAFLD and its complications. Reducing the stigma associated with obesity and liver disease will also play a crucial role in encouraging individuals to seek care early, thereby improving prognoses.
Furthermore, international guidelines must evolve to incorporate the latest research findings and align management strategies with global health priorities. This will help ensure that healthcare systems worldwide are equipped to tackle the challenges presented by NAFLD and HCC in a concerted manner.
NAFLD stands for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, characterized by fat build-up in the liver in people who drink little to no alcohol.
Yes, NAFLD can progress to a more severe disease spectrum, including NASH, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and eventually Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Research has shown that patients with NASH are at the highest risk for developing HCC, particularly when fibrosis is present.
HCC may present with unexplained weight loss, loss of appetite, abdominal pain or swelling, jaundice, or liver dysfunction. Symptoms may not occur until the disease is advanced, underscoring the need for regular screening in at-risk populations.
Maintaining a healthy weight, regular physical activity, balanced diet, and monitoring and managing metabolic risks can help prevent progression from NAFLD to HCC. Engaging in routine screenings and adopting lifestyle changes can also substantially reduce the risk of developing more severe liver conditions.
Key lifestyle changes include achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, incorporating physical activity into your daily routine, adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and avoiding excessive consumption of saturated fats and sugars. Regular monitoring of liver health is also advisable.
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in managing NAFLD. Diets lower in refined carbohydrates and saturated fats, combined with increased omega-3 fatty acids, can significantly improve liver function. Working with a dietitian can provide individuals with tailored nutritional advice based on their health status.
Currently, no specific medications are approved for NAFLD treatment; however, research is ongoing. Medications that target insulin resistance and inflammation are being studied, and emerging therapies aim to address the underlying metabolic issues contributing to NAFLD progression.
Individuals at higher risk for liver disease, particularly those with diabetes, obesity, or existing liver conditions, should discuss screening frequency with their healthcare provider. Generally, biennial liver evaluations may be appropriate for at-risk populations.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
